Solid Waste Management Center
Galigamuwa Pradeshiya Sabha – Live Waste Collection Route
| කසළ එකතු කිරීම (දේවාලේගම මාර්ගය) | කසළ එකතු කිරීම (කොටියකුඹුර දක්වා) | කසළ එකතු කිරීම (ගලිගමුව මාර්ගය) |
| https://chat.whatsapp.com/I5kDOdV3Id3CJtsbMb4loL | https://chat.whatsapp.com/BkwS1lVZgr6FgmS8QPSFAU | https://chat.whatsapp.com/FW2bdgMDNlS8sj7blOGZFr |
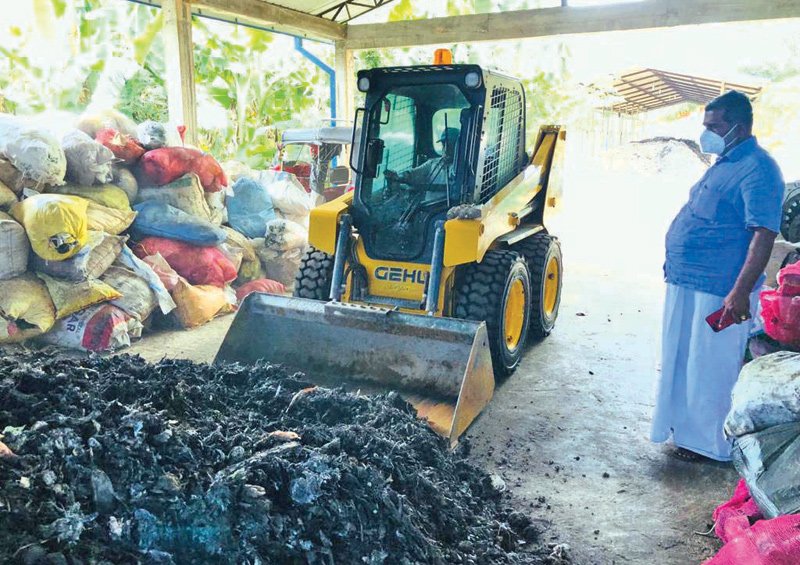


Galigamuwa Pradeshiya Shaba located in Kegalle District of Sabaragamuwa Province has an area of 124.57 square kilometers. Consisting of 51 Grama Niladari Divisions, this jurisdiction has a population of about 78841 (Sampath Pathikada 2021) belonging to Sinhalese, Tamils, Muslims and other ethnic groups. The main livelihood is agriculture and self-employed businesses and public and private sector employees.
According to the powers assigned by the Local Council Act No. 15 of 1987 and according to the by-laws compiled, the local council carries out the matters of garbage collection, transportation and remediation of garbage generated in the Galigamuwa local council area.
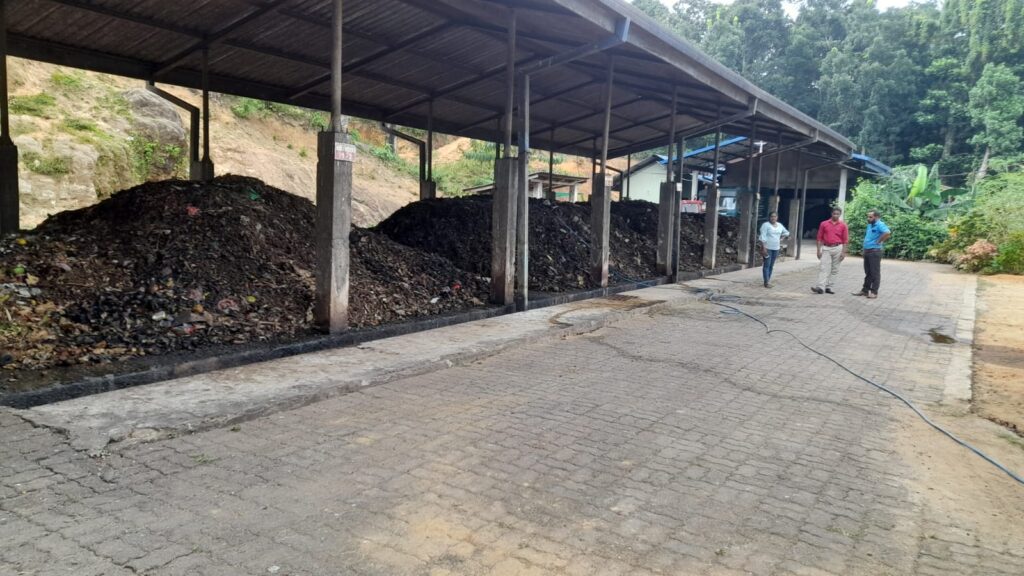
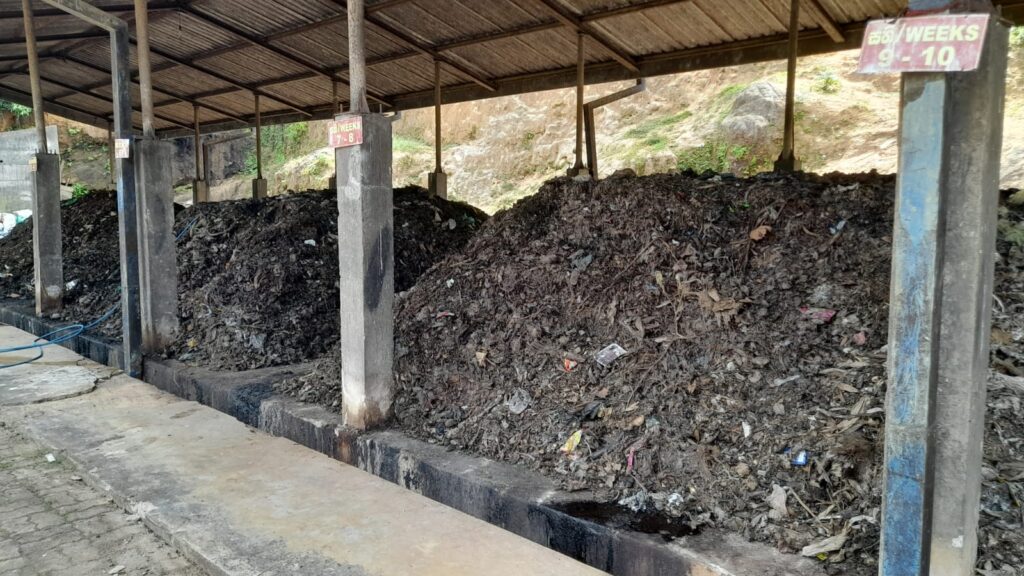
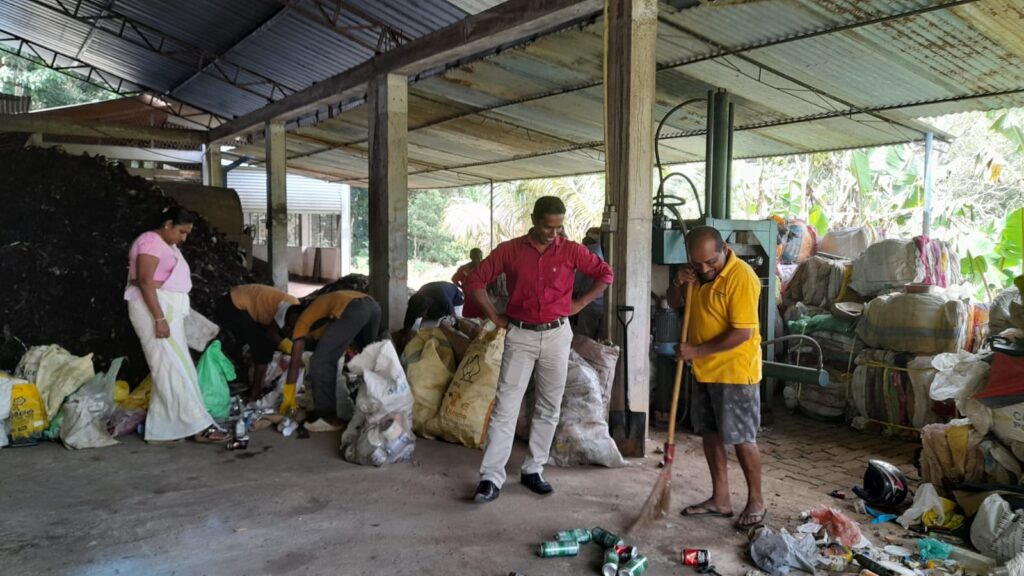
Accordingly, with the aim of creating a clean and healthy environment through the effective and efficient implementation of urban solid waste management, the waste yard was constructed at Hakahinna Taranagala Reserve. There, the main tasks of the solid waste management center are to separate the garbage collected by the local council, the garbage transported to the garbage yard into biodegradable and non-biodegradable, compost fertilizer is produced from the biodegradable garbage, and the non-biodegradable garbage is further divided into glass, solid plastic, PET bottles, Generates income by selling valuable recyclable solid waste like tin and iron. The remaining priceless non-recyclable parts will be baled by the bale machine and delivered to INSEE, a cement manufacturing company, under the coordination of the Local Government Department.
Through these processes, an optimal service is provided to the public by managing the garbage collected daily along 03 main roads in the area.
Current Projects of Solid Waste Management Center
- Compost Production Project
- Baling non-recyclable solid waste using baler machine.
- Running a biogas unit
- Recyclable non-biodegradable solid waste marketing project
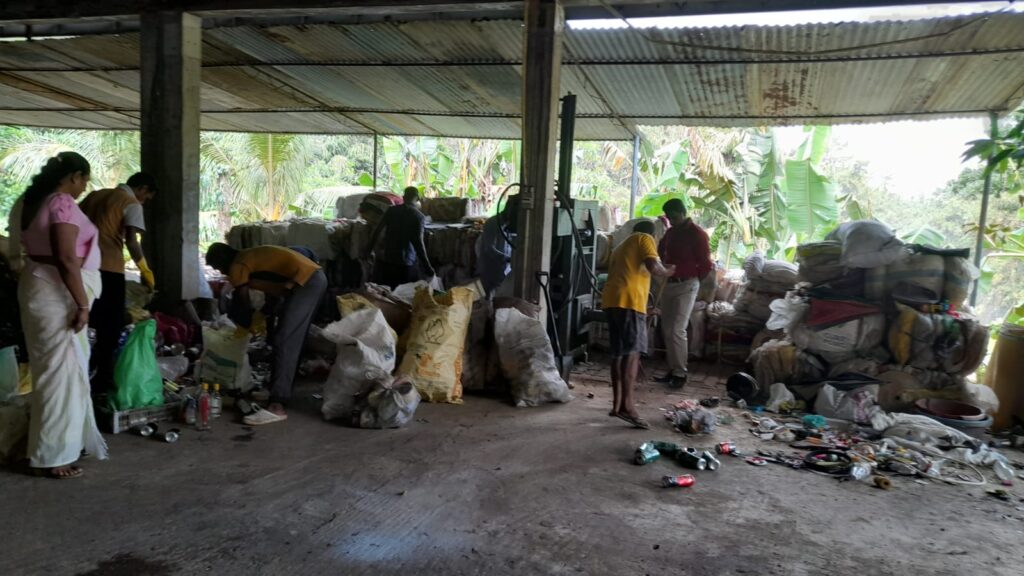
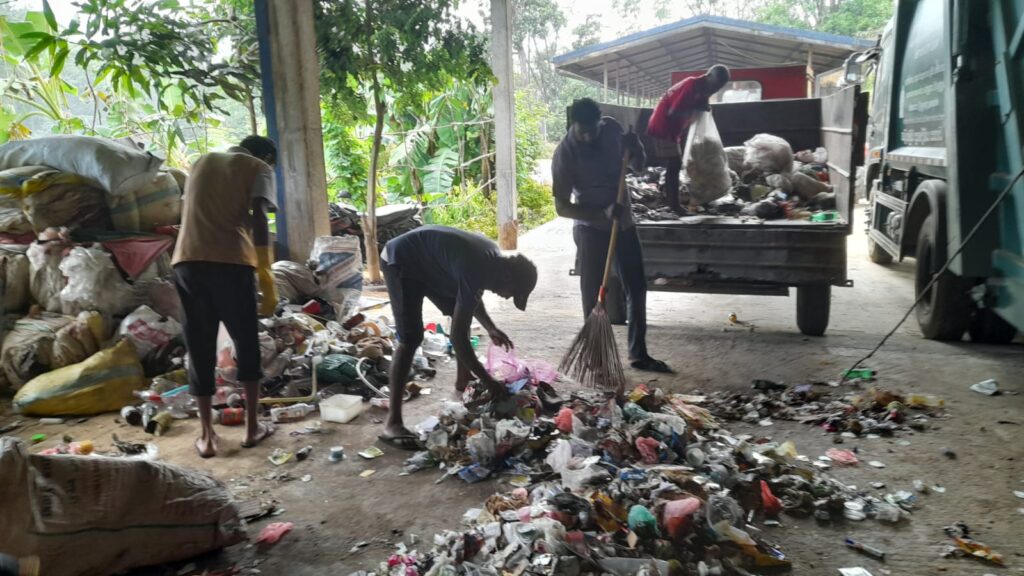








Legal authority
- Section 93 of the Local Councils Act No. 15 of 1987
- The terms and conditions mentioned in the solid waste management by-laws compiled by the Sabaragamuwa Provincial Council
Objectives of maintaining Solid Waste Management Center
- To fulfill the legal role assigned by the Local Council Act No. 15 of 1987.
- Regular collection and disposal of waste generated in the jurisdiction with proper management.
- To maintain the environment of the jurisdiction clean and attractive.
- Production of compost manure and its use for crops in the area.
- Generating income through compost fertilizer production.
- Preventing the spread of infectious diseases in the area.
- Gaining the favor of the people of the jurisdiction by controlling and regularizing the generation of garbage.
Human and physical resources deployed in the solid waste management project
Compost Project Staff
- Driver – 03
- Labor – Permanent – 05
- Casual/Service Contract Basis/Multitasking/Contract – 10
Amount of human and physical resources related to garbage collection
Amount of human resources
- Driver – 03
- Labor – Permanent – 02
- Contract – 04
Amount of physical resources
Garbage collection method of Galigamuwa local council
- Garbage tractors – 03
- Compactor – 01
Route – From the local council office via Galigamuwa Junction, Ambanpitiya, Yattogoda
Areas covered – Narangoda, Naberia, Dematanpitiya, Asidenia, Bisowela, Ballapana Udabage, Ballapana Pathabage, Yattogoda
- Number of tractors deployed – 01
- Driver – 01
- To load labor garbage – 01
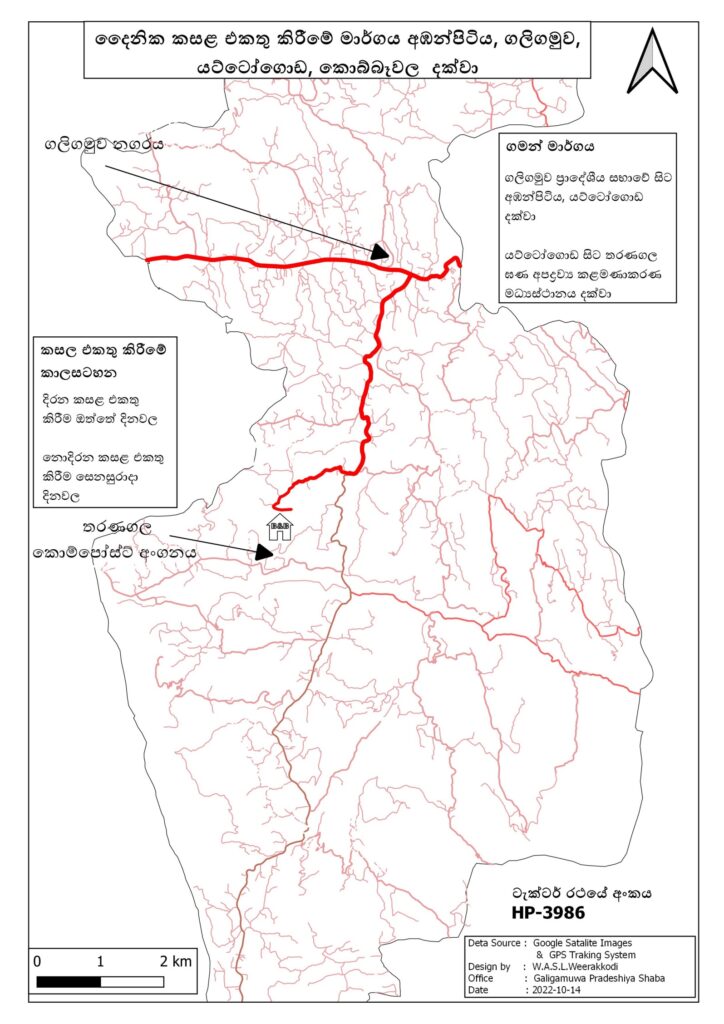
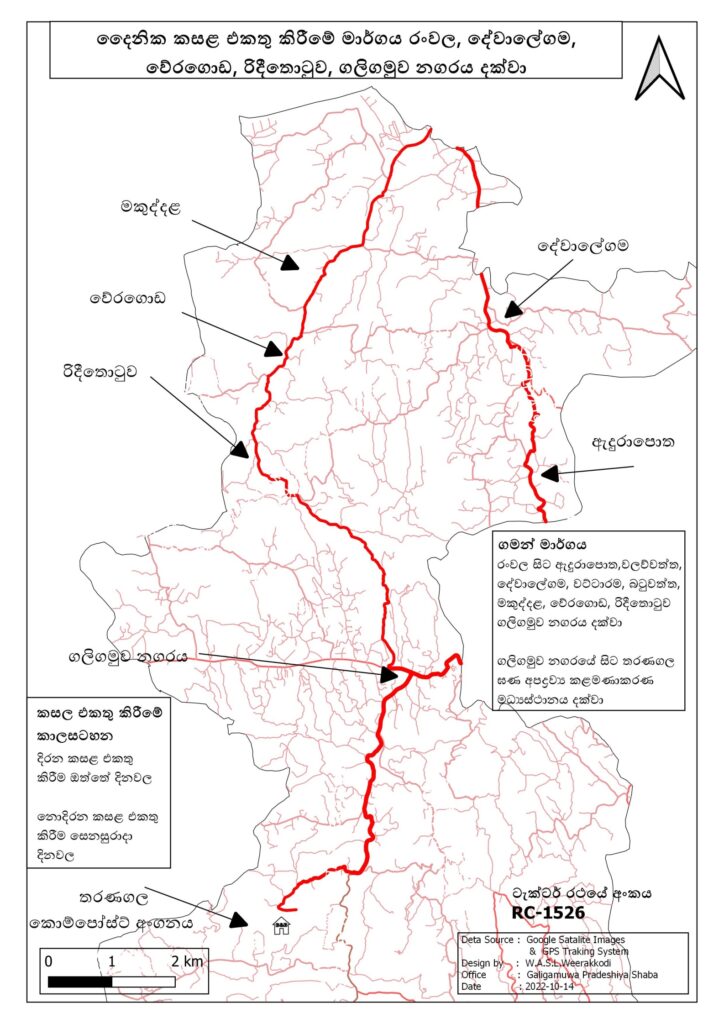
Route – Adurapotha to Dewalegama, Weragoda, Redeethotuwa, Galigamuwa town
Domains covered – Adurapotha, Dewalegama, Wattarama
- Number of tractors deployed – 01
- Driver – 01
- To load labor garbage – 01
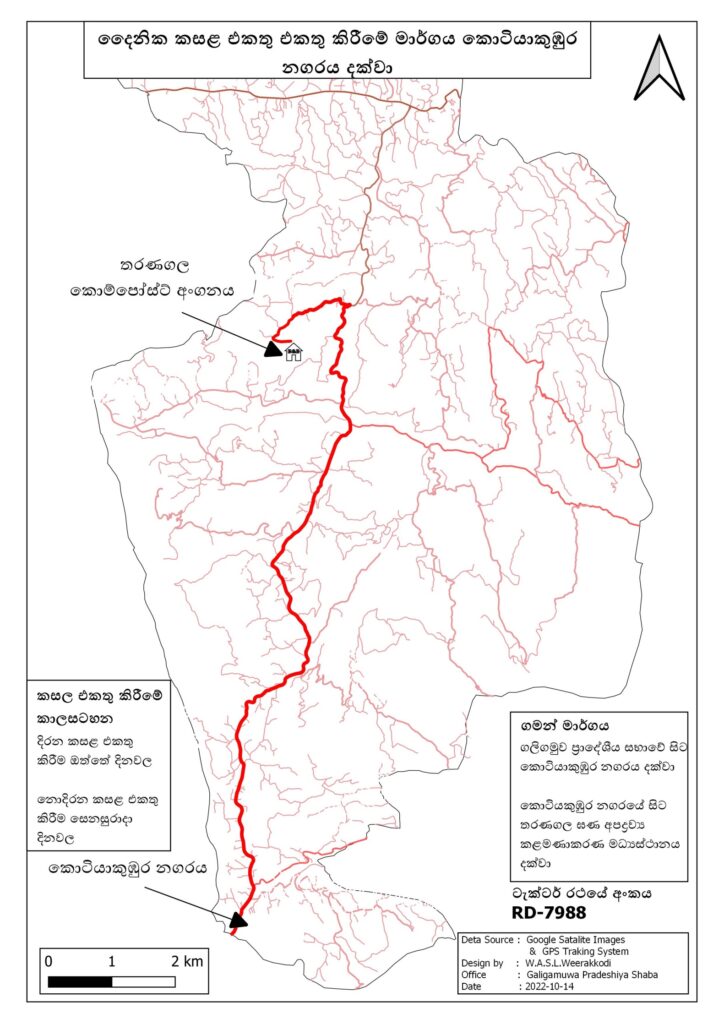
Route – Kotiakumbura town from local council office
Areas covered – Arandara, Nadeniya, Atala, Pindeniya, Kurunegoda, Ampe (Tuesday/Wednesday/Thursday/Saturday/Sunday)
- Number of tractors deployed – 01
- Driver – 01
- To load labor garbage – 01
Common waste generation locations / waste collection sources and quantities
Places where most garbage is generated
| No | location |
| 01 | Access junction to Galigamuwa Industrial Park |
| 02 | Pitgaldeniya Satipola |
| 04 | From large-scale hotels, garment factories, bakeries |
***At present, the above places have adopted various methods of waste disposal and have taken measures to control it.
Sources and quantities of garbage collected
| No | source | Amount (Gross) (Monthly) |
| 01 | Street baiting | Ton 01 |
| 02 | Houses and hotels | Ton 08 |
| 03 | Business locations | Ton 05 |
| 04 | Satipola | Ton 06 |
| 05 | Other | Ton 02 |
*** The above amounts are subject to change from time to time.
Information about solid waste management
Many environmental and health problems have arisen due to the improper disposal of garbage in the urban areas of our country. A solid waste management process has been introduced to provide a solution to that problem. It involves collecting solid waste and recycling it to make various products. Accordingly, at the present time, in many parts of the country, local government agencies are collecting and managing solid waste.
What is solid waste
Solid wastes that are considered to have no economic value and are thrown away from everyday processes are called solid wastes. These include paper, cardboard, glass, plastic, polythene, metals, coconut shells, and various discarded food items. In the last few decades, along with the growth of the population in Sri Lanka, the irregular disposal of solid waste has become common. Therefore, several problems have been created in urban and semi-urban areas.
Environmental and health problems caused by solid waste
- Piles of garbage are seen everywhere due to improper disposal of waste. Then the beauty of the environment is lost.
- Addition of noxious gases to the atmosphere due to burning of garbage heaps.
- Creating a difficult environment for people to live due to excessive stench from garbage heaps.
- Spread of diseases by various animals in the vicinity of garbage collection sites.
- Animals die from eating waste from garbage dumps.
- Due to the accumulation of waste in the water, the drinking water becomes contaminated and unfit for consumption.
Why should waste be managed?
At present, many local government bodies are implementing waste management projects in their jurisdictions, where waste management is done in several ways. Through such waste management
- Beautifying the environment
- Reducing the spread of disease
- Being able to earn money through waste recycling
- Reduction of environmental pollution
- Creating a suitable environment for people to live
It gives positive results to the economy and society in a very good way.
Methods used in waste management
- Recycling of inorganic waste
- The concept of segregation of waste at source
- Community Participatory Domestic Compost Production Systems (e.g. compost bins, biogas units)
- Low rate composting systems for local authorities
Color code system used to separate waste
At present, the concept of separating waste at the point of generation is carried out by many local authorities. The waste separated by that process is used for composting and recycling processes. Different colored bins are used to separate the waste. The color codes used are as follows.
- Blue color – paper and cardboard
- Red color- glass
- Orange color- plastic and polythene
- Brown color- metal and coconut shell
- Green color- Degradable material

Recycling of inorganic waste
Materials such as polythene, plastic, glass, metal, paper and cardboard are classified as inorganic waste. Due to the addition of the above-mentioned substances to the environment, environmental pollution occurs in a big way. Especially the release of plastic and polythene into the environment has become a big problem. Therefore, inorganic wastes are recycled and various useful things are produced. There are people all over the island who contribute to that process. Their duty is to go to villages and buy inorganic waste, take it to recycling centers and sell it at a higher price. In the future, environmental pollution can be controlled through the successful implementation of this program in our country.
Making compost from organic waste
Food waste, green waste, and cuttings are among the organic wastes. In this way, compost fertilizer is produced using the organic waste that is disposed of as garbage. Also, the same organic waste is used to make biogas units. The fertilizers produced in this way are used in agricultural works. Biogas is also used for cooking and lighting purposes. Accordingly, this has become a successful way to save the gas and electricity used in everyday life.
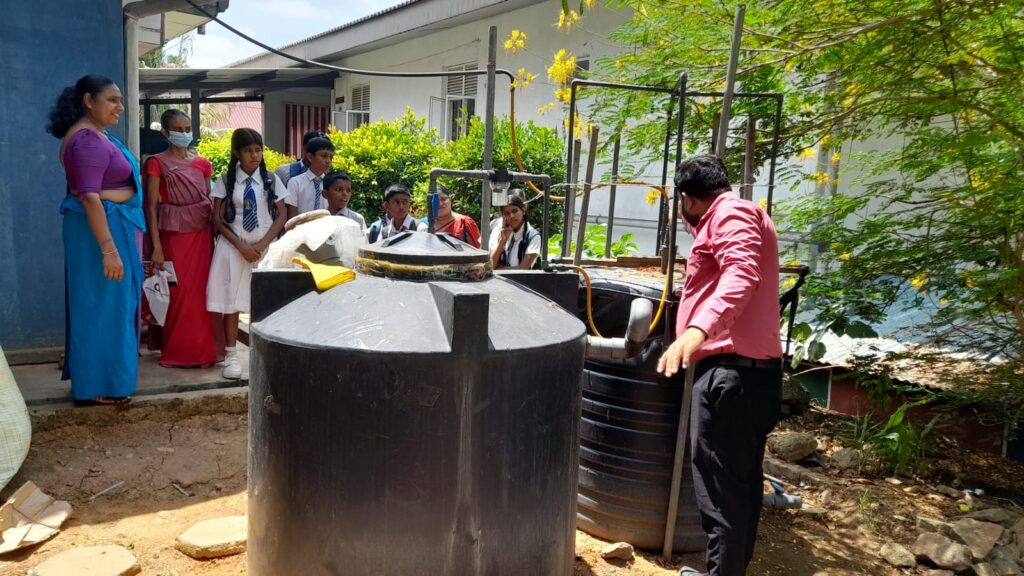
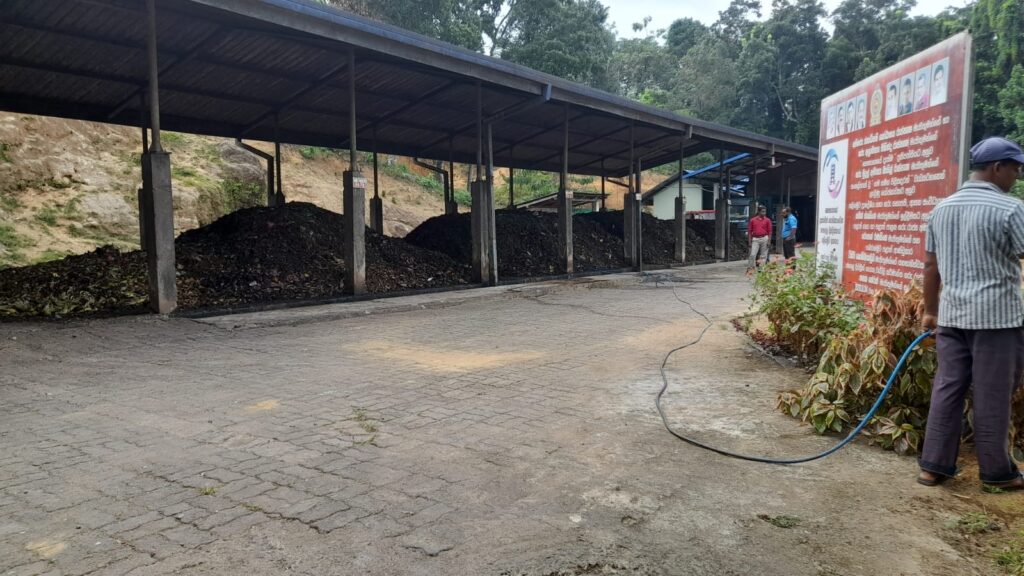


3R concept
The concept of 3R has been introduced to manage solid waste. The three letters R shown in it represent the following three things.
- Reduce
- Reuse
- Recycling
